Diabetes and itching are strongly related to each other. This is because diabetes can cause dehydration and skin dryness, leading to itchiness.
Diabetes-related itching may also cause velvety dark patches on the skin, smooth yellowish bumps, or patches. These symptoms can be caused by skin dryness or a yeast infection.
The itching of your skin may show diabetes, especially if you have other symptoms. High blood sugar levels cause itchy skin. The complications of diabetes, including nerve damage and kidney disease, can cause itchy skin.
This blog post will explain why diabetes can cause itching all over the body. The symptoms of diabetes include itching and tips to manage and treat diabetes-related itching.
Can Diabetes Cause Itching All Over Body: 3 Factors
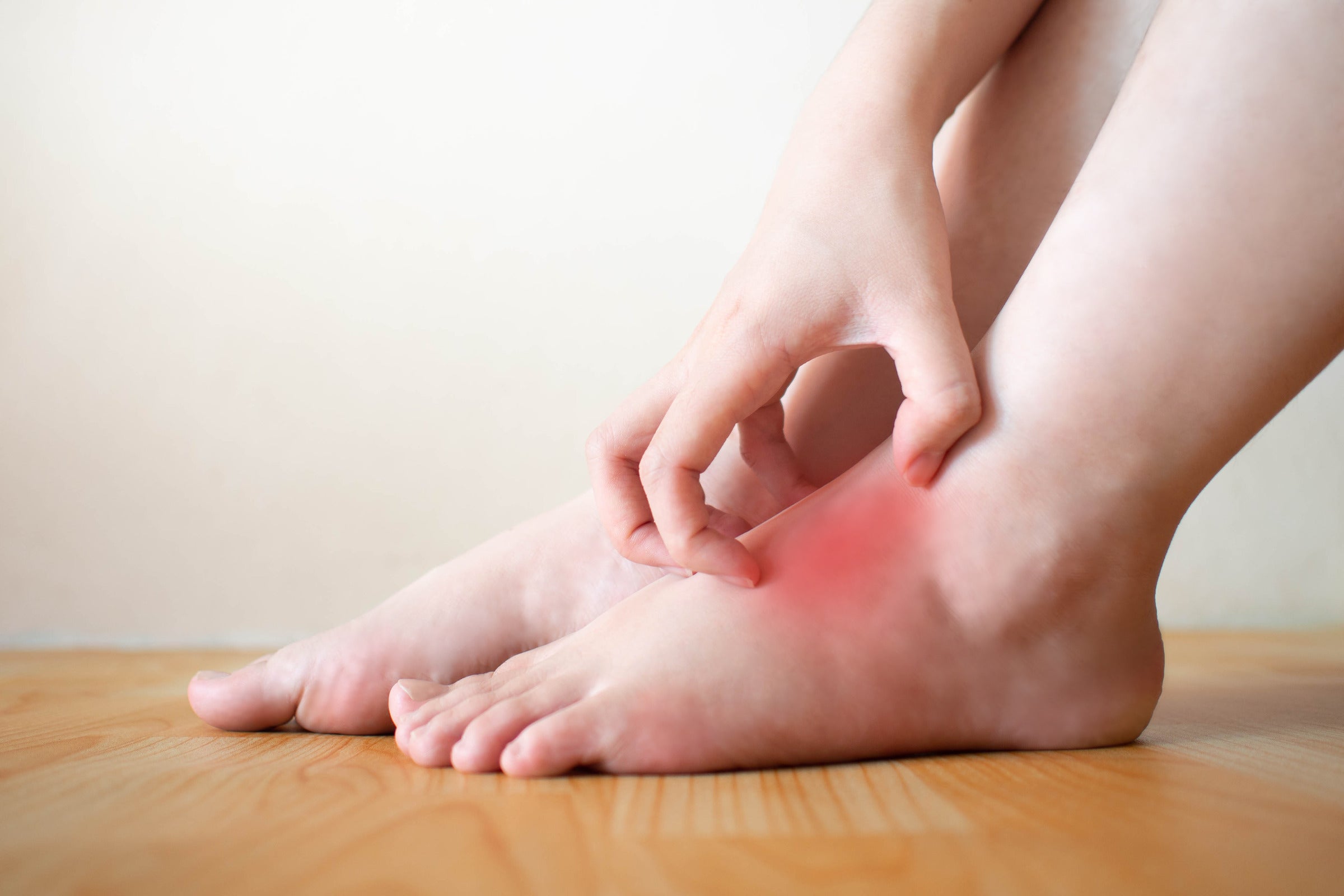
Diabetes is a complex condition that affects multiple body systems. One of the lesser-known side effects of diabetes is itching all over the body, often due to localized issues or nerve damage. Diabetes can cause more itching than others. This discomfort can occur for several reasons:
- Damaged Nerve Fibers: Itching can be caused by damaged nerve fibers in the skin's outer layers. This can happen for various reasons, including skin conditions, allergies, and other underlying medical conditions. Identifying the root cause of itching is essential to treat it effectively.
- Diabetic Polyneuropathy or Peripheral Neuropathy: This condition is characterized by damage to nerve cells resulting from high glucose levels. Mostly affects feet and hands, causing tingling, numbness, and pain. A person's quality of life can be compromised if this goes untreated. Jeopardizes a person's quality of life.
- High Level of Cytokines: some observe that in individuals with diabetes, elevated levels of cytokines, which are inflammatory agents, can be found in the body before the onset of nerve damage. This heightened presence may cause itching sensations.

Itching as a 6 Symptoms of Diabetes
People with diabetes may experience more frequent and intense itching than those without the condition. This itching can be localized to specific areas or spread across the entire body, causing considerable discomfort. There are several reasons this happens:
- High Blood Sugar Levels: Diabetes can cause high blood sugar levels, leading to dry skin and itching. With high blood sugar, your body loses fluid, leading to dehydration and dry skin.
- Poor Circulation: Diabetes often leads to poor circulation, especially in the lower limbs. Poor circulation can cause itching, particularly in the legs and feet.
- Nerve Damage: Diabetic neuropathy, a condition caused by sugar damage, can also cause itching. This usually occurs in the hands and feet.
- Yeast Infections: People with diabetes are more susceptible to yeast infections because of high sugar levels, which provide a favorable environment for yeast growth. These infections can cause itching in the affected areas.
- Skin Conditions: Diabetes can lead to certain skin conditions that cause itching. These include diabetic dermopathy (brown patches on the skin), necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum (similar to diabetic dermopathy but with more extensive and fewer patches), and eruptive xanthomatosis (firm, yellow, pea-like skin growths).
- Kidney or Liver Complications: If diabetes has led to kidney or liver complications, these conditions can also cause itching.
Managing and Treating Diabetes-Related Itching: 5 Tips
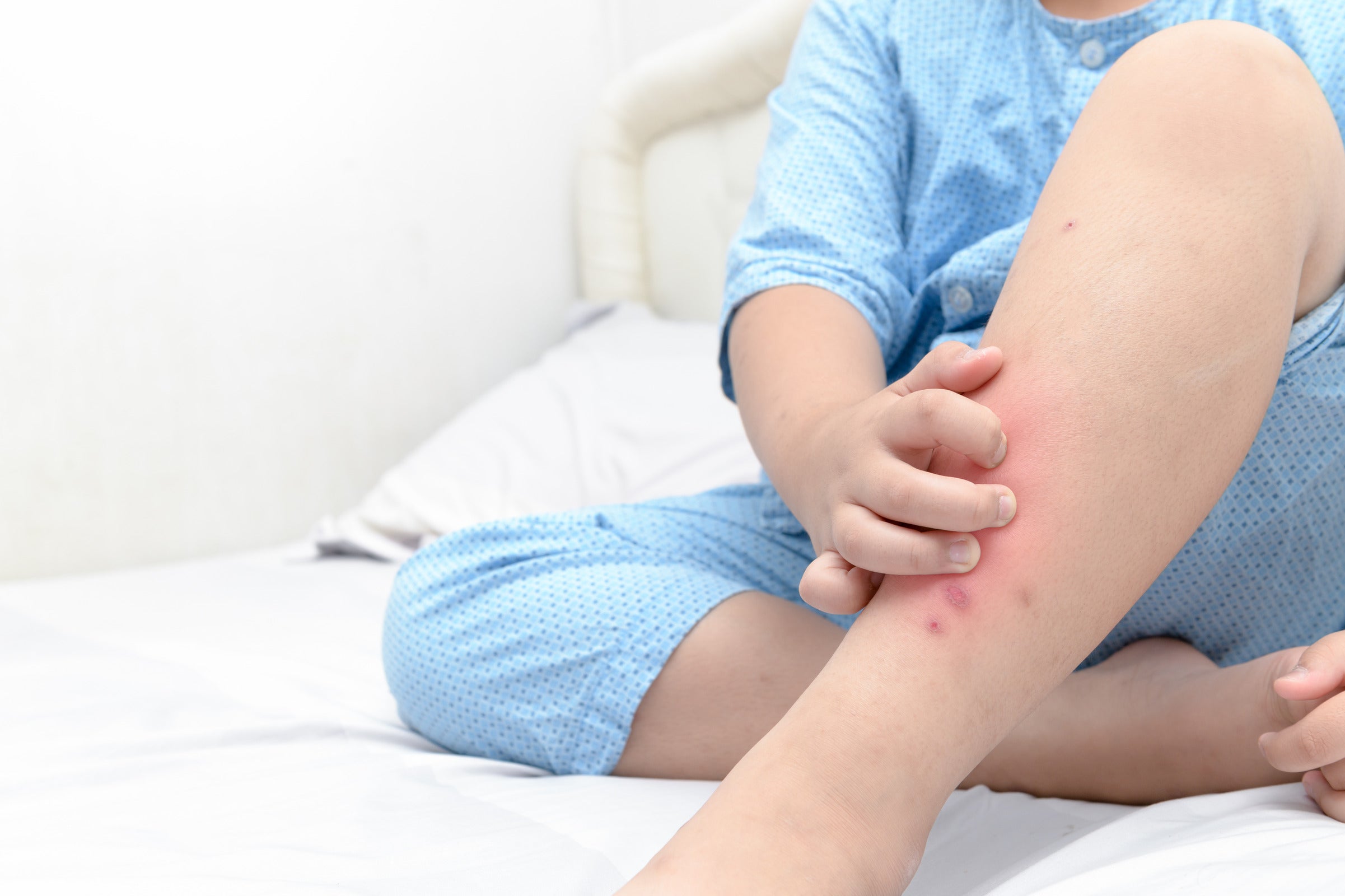

While dealing with diabetes-related itching can be challenging, there are several ways to manage this symptom:
- Control Blood Sugar Levels: Keeping your blood sugar levels in check is the first step to reducing itching. Regular monitoring and proper medication can help maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
- Skin Care: Regular skin care can ease dryness and itching. Use mild soaps, avoid hot showers (which can dry out your skin), and apply moisturizers regularly.
- Healthy Lifestyle: A healthy lifestyle, which includes a balanced diet and regular exercise, can enhance circulation and reduce itching.
- Medication: Sometimes, your healthcare provider may prescribe medication to control itching. Several medications, including antibiotics and antifungal drugs, may lead to itchy skin.
- Regular Monitoring: Regularly checking your blood sugar levels makes it easier to manage your diabetes. It allows you to adjust your diet, exercise, and medication.

Conclusion
While diabetes may seem daunting with surprising facets like full-body itching, understanding is the first step to overcoming it. This bothersome itch can result from high blood sugar levels, poor circulation, nerve damage, and various skin conditions.
With the right lifestyle choices, consistent blood sugar management, regular skin care, and a keen eye on your situation, you can combat this itchy problem.
Let's scratch this problem off your list so that the focus can be on living your best, healthiest life with diabetes. Stay tuned and eager to learn more about managing diabetes and its unusual side effects.















![The Most Common Food Allergies That Cause Itchy Skin [6 Common Symptoms]](http://drnumb.ca/cdn/shop/articles/Can_Food_Allergies_Cause_Itchy_Skin__17_Listed_6_Symptoms_Common.jpg?v=1714999986)



